Currently Empty: 0,00 د.إ
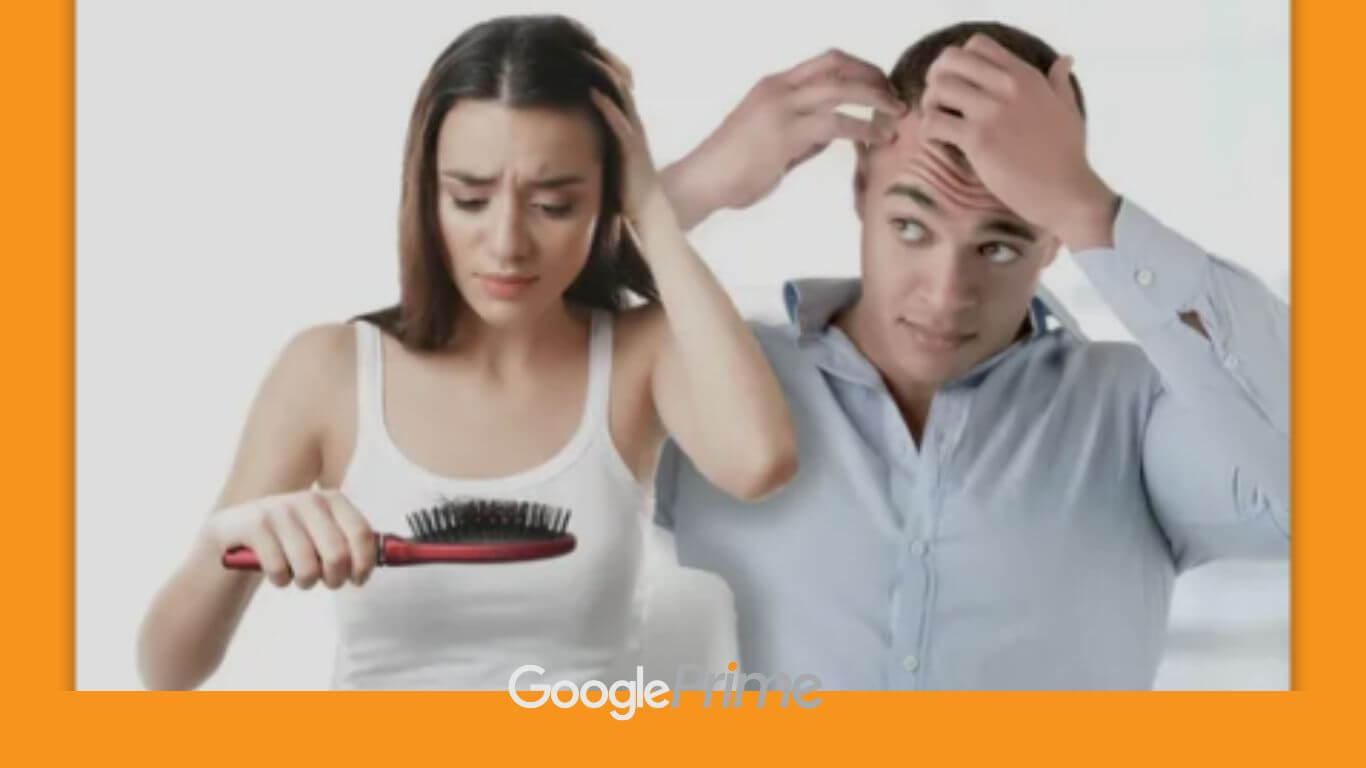

Hair loss, also known as alopecia, can impact your scalp or entire body, and be temporary or permanent. It can stem from genetics, hormones, medical conditions, or simply aging. While anyone can experience hair loss, it’s more prevalent in men. Recent surgery, fever, or childbirth can also trigger temporary shedding.
It is normal for some hair to shed daily. Losing up to 70 – 100 hairs daily is normal
Google Prime Dermatologist
While male and female pattern baldness are the leading causes of hair loss, other conditions and lifestyle factors can also contribute. A dermatologist will need to investigate these potential causes to recommend the most suitable treatment.
Symptoms
Hair loss can manifest in various ways depending on the cause, appearing suddenly or gradually, and affecting just the scalp or the entire body. Recognizing the symptoms early can help in finding effective treatment.
- Male-pattern baldness
- Female-pattern baldness (alopecia)
- Patchy hair loss (alopecia areata)
- Traction alopecia (Traction)
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA)
Male-pattern baldness

Male pattern baldness typically starts with a receding hairline at the front of the head, gradually forming an ‘M’ shape. Additionally, a circular area at the back of the head (vertex) often begins to thin and expands over time.
Androgenetic Alopecia Treatment Options
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, can be managed with various treatments. One popular option is minoxidil (Rogaine, Loniten), a topical medication that stimulates hair growth. While results may vary, noticeable hair improvement often occurs within six to twelve months of consistent use.
Additional treatment avenues include:
- Medications: Finasteride (Propecia) is effective for male pattern baldness, while spironolactone (Aldactone) can help manage female hair loss.
- Laser Therapy: Low-level laser therapy stimulates the scalp to promote hair growth.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp to encourage hair regeneration.
- Hair Transplant: A surgical procedure where healthy hair follicles are relocated to thinning areas.
- Nutritional Supplements: Certain supplements may support hair health, but their effectiveness varies.
Note: It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment option for your specific condition.
Female-pattern baldness
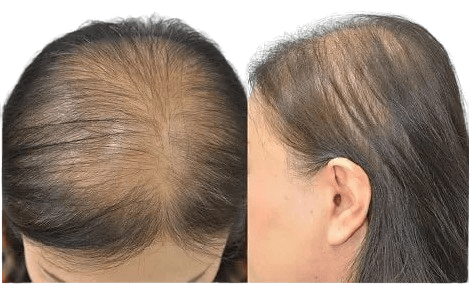
Female pattern baldness, the most common form of hair loss in women, is influenced by hormones, aging, and genetics. Unlike male-pattern baldness, it involves overall hair thinning while preserving the normal hairline.
Temporary hair loss can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Stress, illness, and childbirth: These conditions can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as chemotherapy agents, blood thinners, and birth control pills, can lead to temporary hair loss.
- Physical trauma: Burns, injuries, and radiation exposure can cause temporary hair loss.
- Autoimmune diseases: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that attacks hair follicles.
Patchy hair loss

Alopecia areata primarily targets the head and face. Typically, hair falls out in small, round patches about the size of a quarter, but it can sometimes lead to more extensive hair loss. Most individuals with alopecia are otherwise healthy and experience no additional symptoms.
Traction alopecia
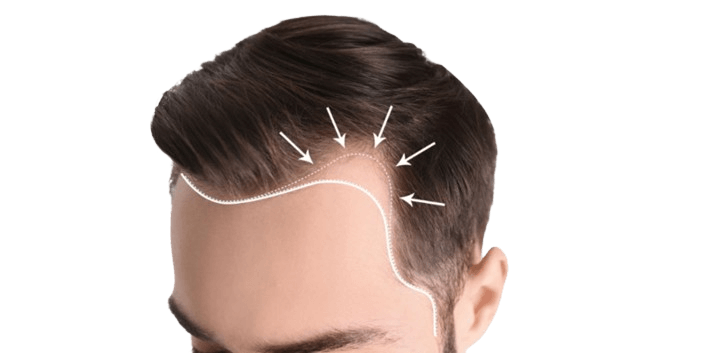
Traction alopecia is a form of hair loss resulting from continuous pulling on the hair. This repeated tension, often from tight hairstyles, causes certain hairs to be pulled more than others, leading to the formation of bald patches
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA)
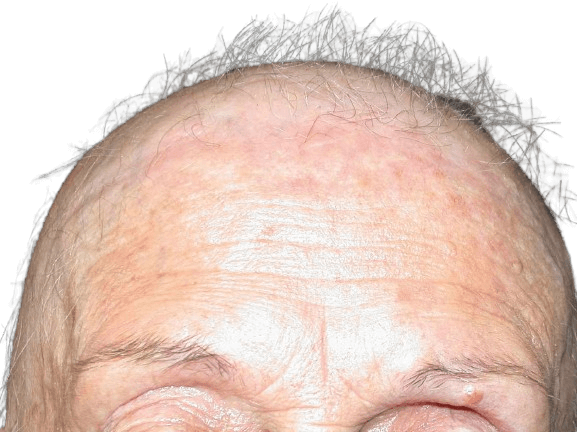
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) results in hair loss at the front and sides of the scalp, and can also impact the eyebrows, eyelashes, and other areas of the body. This condition may stem from autoimmune reactions, genetic predisposition, or hormonal influences.
Myths

Hair loss myths abound. Let’s debunk some:
- Wearing a baseball cap or hat may cause “hat hair,” but it does not cause hair loss.
- Baldness is genetic. It can come from either parent.
- Supplements won’t regrow hair. Healthy diet helps maintain hair.
- Testosterone levels don’t cause baldness. DHT hormone is key.
- Stress causes temporary hair loss. Not permanent baldness.
- Sun exposure doesn’t cause baldness. But it damages hair.
- Hair restoration treatments can work. Finasteride, Rogaine, and transplants are options.
Lifestyle Tips for Healthier Hair
Maintaining a healthy hair routine involves more than just products. Lifestyle factors significantly impact hair growth and overall hair health. Here are some tips to help prevent hair loss and promote thicker, stronger hair:
Additional Tips
- Limit smoking and secondhand smoke: These harmful substances can negatively impact hair health.
- Protect your hair from the sun: Excessive sun exposure can damage hair. Wear a hat or use hair products with SPF when spending time outdoors.
- Regular scalp care: A healthy scalp promotes hair growth. Gently massage your scalp to improve blood circulation.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Nourish Your Body: Eat a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins and minerals report 2018.
- Gentle Hair Care: Avoid harsh hairstyles and heat styling.
- Product Selection: Use gentle, lightweight hair care products.
While these lifestyle changes can help prevent hair loss and improve hair condition, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and to rule out underlying medical conditions.
For those experiencing noticeable hair loss, consider exploring options like scalp concealers or hair toppers as temporary solutions.
By adopting these habits and seeking professional guidance, you can take significant steps toward healthier, fuller hair. Explore the latest hair loss solutions subscribe Google Prime.
Frequently asked questions
Below are some frequently asked questions about hair loss.
What Are the Main Causes of Hair Loss?
Male and female pattern baldness are the primary causes of hair loss. However, other factors, including tight hairstyles and medical conditions like alopecia, can also lead to hair loss.
Which Vitamin Deficiency Can Cause Hair Loss?
Vitamin D deficiency may be linked to hair loss. Additionally, individuals with low iron levels can benefit from iron supplementation and ensuring adequate vitamin C intake to help prevent hair loss.
What Foods Help Prevent Hair Loss?
Very low protein diets can cause restricted hair growth and hair loss. Collagen, the main structural protein in hair, helps strengthen the hair shaft and prevent breakage. To support hair health, include protein-rich foods like chicken, turkey, fish, dairy products, eggs, legumes, and nuts in your diet.
- Chicken
- Fish
- Dairy Products
- Eggs
- Legumes (beans, chickpeas, peanuts, lentils, lupins, mesquite, carob, tamarind, alfalfa, and clover)
- Nuts
- Fruits rich in Vitamin C – Oranges, Grapes, Berries, Cherries.
How Can Someone Prevent Hair Loss?
The following lifestyle changes may help prevent hair loss:
- Reduce stress through activities like meditation or massage
- Maintain a balanced diet
- Avoid tight hairstyles
- Limit the use of heat-based hair styling products, such as curling irons
- Brush hair gently



1 Comment
Thanks for sharing